Netboot Products
Netboot products can be used independently of the installed operating system, providing maximum flexibility for various use cases. Typical applications include reinstalling operating systems, diagnostics, or maintenance tasks. Execution is usually performed via the opsi-linux-bootimage – a Linux distribution specially developed and adapted for opsi. GRUB2 is used as the bootloader. For Secure Boot operation, a shim is used.
By default, the opsi-linux-bootimage is started via PXE boot. Alternatively, a ISO file is available, which can be booted from CD or USB stick. This allows netboot products to be used in environments where PXE is not available.
Netboot products can also provide their own boot images, which are also started via PXE. Examples include MemDisk or the security tool Desinfec’t.
Control of PXE boot is handled by the opsipxeconfd service on the opsi depot server. Additionally, a DHCP server and a TFTP server are required.
Configuration of the Netboot Environment
The netboot environment is mainly configured via host parameters with the prefix netboot..
These parameters can be set depot-wide (for all clients of a depot) or client-specific (only for a particular client).
| Client-specific settings currently only apply if an action for a netboot product is set for the client. |
Important host parameters for netboot behavior:
netboot.use_host_onetime_password-
During network boot, the client authenticates with the opsi service. By default, the opsi host key is used for this. If this parameter is set to
true, a one-time password is used instead, increasing security. netboot.host_identifiers-
Defines how clients are identified during network boot. Possible values are:
-
mac_address(MAC address of the network card) -
system_uuid(system UUID of the client)
-
Both values can be combined. Depending on the selection, a configuration file is created in the boot directory, based either on the system UUID or the MAC address.
netboot.grub.additional_menu_entries-
Allows adding further menu entries to GRUB2.
netboot.grub.graphicsmode-
Enables or disables the graphics mode of GRUB2.
netboot.grub.password-
Sets a password for accessing the GRUB2 menu. The username is always
admin. The password can be specified in plain text or as a hash (grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.<salt>.<hash-value>). Hash values can be generated, for example, withgrub-mkpasswd-pbkdf2. netboot.grub.timeout-
Specifies how many seconds the GRUB2 menu is displayed before the default entry is automatically started (if no action for a netboot product is set).
Parameters for the Linux Bootimage
All parameters with the prefix netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline. are passed as kernel parameters to the opsi-linux-bootimage.
Both regular Linux kernel parameters and special parameters supported by the opsi-linux-bootimage can be used.
There are two types of host parameters:
- Boolean host parameters
-
These serve as flags. They are added to the kernel command line if set to
true. If set tofalse, they are not passed. - String host parameters
-
These are passed as
<parameter name>=<value>to the kernel command line. Multiple values are separated by commas. If no value is set, the parameter is not passed.
Additional kernel parameters can be added at any time by defining corresponding host parameters with the prefix netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline..
Important kernel parameters in connection with opsi:
hn-
Sets the system hostname.
dn-
Sets the domain name.
host_id-
Sets the opsi host ID of the system.
service-
Address of the opsi service to connect to.
pckey-
opsi host key for authentication.
otp-
One-time password for authentication (alternative to pckey).
opsi_ui-
Selection of the opsi user interface (splash or tui). Default is splash.
lang-
Sets the system language. Format:
<language>[_Region][.charset](e.g.de,de_DE,de_DE.UTF8). tz-
Sets the timezone, e.g.
Europe/Berlin(default isUTC). pwh-
Password or password hash for the root user (
$<hash-type>$<salt>$<hash>). macaddress-
Assigns a custom MAC address to the network device.
nodhcp-
Disables DHCP configuration for network devices.
dhcp_identifier-
Determines the DHCPv4 client identifier (
macorduid). Default ismac. ssh-
Starts the SSH service at boot.
splash-
Enables the graphical splash screen during boot.
tcpdump-
Enables network packet capture in
/tmp/tcpdump.pcap. Additional options are passed as arguments to tcpdump. opsi_loglevel-
Sets the opsi log level (0-9).
product-
Specifies the ID of the netboot product to be processed.
ask_conf-
Prompts the user interactively to confirm configuration values.
Other relevant kernel parameters:
quiet-
Suppresses most kernel and system messages during boot.
loglevel-
Sets the kernel log level (0-7).
video-
Configures the framebuffer.
vga-
Sets VGA resolution and color depth.
noapic-
Disables the I/O APIC (I/O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller).
irqpoll-
Enables IRQ polling for problematic hardware.
pci-
Options for the PCI subsystem.
mem-
Specifies the amount of memory to be used by the kernel.
acpi-
Controls the behavior of the ACPI subsystem.
reboot-
Specifies the method for rebooting.
efi_no_storage_paranoia-
Disables the safety check for reserved storage space in EFI NVRAM (default 5120 bytes under Linux 6.14.0). Warning: This parameter should only be used if it is ensured that the firmware properly cleans up storage according to the UEFI specification. Otherwise, there is a risk of rendering the motherboard unusable.
Debugging and Troubleshooting During Boot
Since booting a netboot product involves several services and components, problems can occur at various points. First, check whether you are using the latest versions of the opsi components.
DHCP
The DHCP server assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to clients. It also provides information about the boot server and boot file required for PXE boot. See Troubleshooting DHCP for troubleshooting DHCP issues.
TFTP
The TFTP server provides the boot files needed by the client to start. Usually, the TFTP server runs on the opsi depot server. See Troubleshooting TFTP for troubleshooting TFTP issues.
GRUB2
GRUB2 is the bootloader used by opsi. If the boot process fails at this point, check the following:
-
Is there a newer BIOS or UEFI firmware for the device?
-
Is the firmware correctly configured (e.g. boot order, Secure Boot settings)?
-
Does booting work with Secure Boot disabled?
-
Disable the graphics mode of GRUB2 (set host parameter
netboot.grub.graphicsmodeto false). -
Test booting the opsi-linux-bootimage via USB stick or CD.
A debug version of GRUB2 is also available.
It provides more detailed information during the boot process and does not automatically continue execution.
The debug variants can be found under <boot>/opsi/loader/grub-debug.<arch>.<efi|bios> and can be used either by adjusting the symlinks or by configuring the client’s DHCP settings accordingly.
opsi-linux-bootimage
If the boot process fails when starting the opsi-linux-bootimage, check the following:
-
Disable quiet mode and the splash screen (set host parameters
netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.quietandnetboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.splashto false). -
Increase the log level of the Linux kernel (set host parameter
netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.loglevelto 7). -
Test booting with different kernel parameters (e.g.
acpi=off,noapic,irqpoll,pci=nomsi,mem=2G).
To log in to the running boot image, you can switch to one of the TTYs 3-6 (e.g., with Ctrl`Alt`F3).
Log in with the username root and the password set in the host parameter netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.pwh.
You can display the system log with the command journalctl.
The kernel log is available via dmesg.
To analyze the status of the network, you can use the commands networkctl status --all, ip l, and ip a, for example.
If the error only occurs when processing the Netboot product, you can check the log file of the boot image.
This is located under /tmp/log in the running boot image.
If possible, the log file is also transferred to the opsi-Configserver and can then be viewed via opsi-configed, for example.
If an opsi Messagebus connection exists, you can open a terminal on the client via opsi-Configed or opsi-cli.
Access is also possible via SSH.
To do this, the parameter netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.ssh must be set to true.
The username for SSH access is root.
The password set under netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.pwh is used as the password.
Special PXE Boot Configurations
By default, netboot products are executed via the opsi-linux-bootimage. However, it is also possible to integrate custom boot images by creating an individual PXE boot configuration.
For this, the pxeConfigTemplate attribute can be used in the metadata of the netboot product.
This attribute allows you to store a GRUB2 configuration template, which is automatically included in the GRUB2 configuration when the netboot product is started.
The templates are based on Jinja2 and can access various variables, including:
host-
The Host object of the client. All attributes are available, e.g.
host.id,host.description,host.hardwareAddress,host.systemUUID. product-
The Product object of the netboot product. Available attributes include
product.id,product.name,product.description. product_on_depot-
The associated ProductOnDepot object.
product_on_client-
The associated ProductOnClient object.
product_property_states-
The ProductPropertyState objects of the product for the client as a dictionary. Access via
product_property_states["<property_id>"]. If the property does not exist, a placeholder object is returned. The following attributes are available:-
id: ID of the ProductProperty. -
exists: Indicates whether the ProductProperty exists. -
values: The set values as a list of booleans or strings. -
str_value: The set values as a comma-separated string. -
bool_value: The set value as a boolean. -
password_hash(method, format): Returns the value as a password hash.-
method:md5,sha512orpbkdf2-sha512. -
format:shadow,grub
-
-
cmdline(pattern, remove_prefix): Generates Linux kernel parameters as a string.-
pattern: A single or a list of Unix wildcards to filter property names. -
remove_prefix: A single or a list of prefixes to be removed from the property name.
-
-
config_states-
All ConfigStates of the client that start with
netboot.as a dictionary. The same attributes as forProductPropertyStateobjects are available. opsi-linux-bootimage-
A special object that provides the method
cmdline(additional_params, config_id_prefix), which generates all required Linux kernel parameters as a string.-
additional_params: Additional kernel parameters as a dictionary that are added or overwritten. -
config_id_prefix: Prefix of config IDs to be added as kernel parameters (default isnetboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.).
-
Alternatively, a directory name can also be specified in pxeConfigTemplate.
In this case, the file grub.cfg from the directory <boot>/opsi/<directory name> will be loaded.
Example for a pxeConfigTemplate attribute:
if [ "$grub_platform" = "efi" ]; then
menuentry 'Start {{ product.name }}' --unrestricted {
echo "Loading {{ product.name }} {{ product.productVersion }}..."
linux (${bootsrc})/opsi/my-product/loader.efi {{ product_property_states.cmdline("cmdline.*", "cmdline.") }}
}
else
echo "{{ product.id }} does not support Legacy BIOS booting."
sleep 5
exit
fiSetting Bootimage Parameters with opsi-cli
With opsi-cli, bootimage parameters can be conveniently set. Passwords can be directly converted into secure hashes.
opsi-cli bootimage set-boot-password <PASSWORD>The password hash is automatically stored in the host parameter netboot.opsi-linux-bootimage.cmdline.pwh and additionally displayed on the console.
Automatic Operating System Installation
Preconditions
The device should be configured for network boot (PXE boot). Alternatively, booting from CD or USB stick is possible.
The opsi package for the desired operating system must be installed on the opsi server.
Network Boot
-
The device starts via PXE boot.
-
The DHCP server assigns the device an IP address and provides boot server (usually opsi depot server) and boot file information.
-
The client loads the boot file from the boot server, depending on architecture and BIOS type (UEFI / Legacy BIOS).
-
If Secure Boot is enabled, the shim is loaded, which then starts the GRUB2 bootloader.
-
Without Secure Boot, GRUB2 is loaded and started directly.
-
GRUB loads the embedded configuration file.
-
The client-specific GRUB configuration file
<SystemUUID>.cfgor<MAC address>.cfgis loaded. These files are dynamically created by the opsipxeconfd service. -
Kernel and initramfs of the opsi-linux-bootimage are loaded from the boot server.
-
The kernel starts with the boot parameters from the GRUB configuration file.
-
The Linux bootimage configures the network interfaces via DHCP.
-
The opsi service of the bootimage starts and connects to the opsi service.
-
The installation configuration is retrieved from the opsi service.
-
A connection to the opsi depot server is established to load the installation files.
-
The script stored for the selected action is executed.
All further steps depend on the respective netboot product. The following describes the process for unattended installation of Windows operating systems under UEFI.
Unattended Installation of Windows Operating Systems
If the ProductProperty askBeforeInst is set, the start of the reinstallation must be confirmed.
- Preparation of the hard disk
-
The hard disk is partitioned. At least one EFI partition (FAT32), one NTFS partition for Windows PE, and one NTFS partition for the operating system are created and formatted.
- Copying installation files
-
The Windows PE stored in the netboot product, the installation files, the appropriate Windows drivers, and the opsi-client-agent are copied from the opsi depot server to the local disk.
- Creating configuration files
-
Various configuration files for the installation are created, including the
unattend.xmlas the control file for the Windows installation. - Adjusting the boot configuration
-
The UEFI boot configuration is adjusted so that the next boot is from the Windows PE partition.
- Windows Setup
-
After reboot, Windows PE starts and performs the automatic installation of the operating system via Windows Setup.
- Installation of the opsi-client-agent
-
During the Windows installation, the opsi-client-agent is also installed and configured. Afterwards, the opsi-client-agent installs further localboot products that are set to
installedorsetup.
ProductProperties of Windows Netboot Products
The Windows netboot products are designed to enable the most flexible and customizable installation of Windows operating systems. Control of the installation is carried out via various ProductProperties, which are described below.
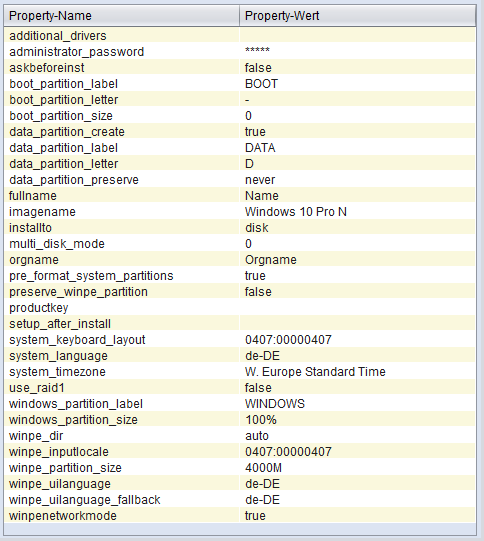
- additional_drivers
-
List of directories under
<depot-share>\<product-id>\drivers\drivers\additional. All driver directories under the specified directories are included in the installation in addition to automatic driver detection. - administrator_password
-
Here you can specify the password to be set for the local administrator during installation.
- askbeforeinst
-
Should confirmation be required before installation?
- boot_partition_size
-
Size of the boot partition (Bitlocker partition). If set to
0, no boot partition is created. - boot_partition_label
-
Label of the boot partition (Bitlocker partition)
- boot_partition_letter
-
Drive letter of the boot partition (Bitlocker partition)
- data_partition_create
-
Should a separate data partition be created?
- data_partition_label
-
Label of the data partition.
- data_partition_letter
-
Drive letter of the data partition.
- data_partition_preserve
-
Should an existing data partition be preserved during reinstallation?
- fullname
-
Full name of the licensee, as passed to the installation.
- imagename
-
Name of the operating system variant to be installed.
- installto
-
This setting is not editable. It is used during the process to distinguish between standard (
disk), opsi-local-image (oli), and opsi-vhd (vhd). - multi_disk_mode
-
This property is used to select the disk to install to. Possible values are:
0,1,2,3,prefer_ssd, andprefer_rotational. Values0,1,2,3specify the disk index directly (0= 1st disk). The valueprefer_ssdselects the first SSD. The valueprefer_rotationalselects the first rotating hard disk (HDD). On systems with only one disk, the ProductProperty is ignored. - orgname
-
Full name of the licensee’s organization, as passed to the installation.
- pre_format_system_partitions
-
Should previous partitions be formatted to remove traces of previous installations?
- preserve_winpe_partition
-
Should the Windows PE partition be preserved after OS installation?
- productkey
-
License key for installation. Only used if the host parameter
license-management.useis set to 'false'. Otherwise, a license key is obtained from license management. - setup_after_install
-
Which localboot products should be installed after the operating system?
- system_keyboard_layout
-
Language selection for the keyboard.
- system_language
-
Language selection for the system.
- system_timezone
-
Timezone setting
- use_raid1
-
Should a software RAID1 be created?
- windows_partition_label
-
Label of the system partition (
C:) on which the operating system is installed. - windows_partition_size
-
Size of the system partition (
C:). The specification can be percentage of the disk or as an absolute number (G=Gigabyte). The remaining space is used for the data partition. - winpe_dir
-
The Windows PE directory used for installation. The value
autoselects the directory automatically. Other values must point to a valid directory in the netboot product. - winpe_inputlocale
-
Input language used under Windows PE.
- winpenetworkmode
-
If this value is
true, the depot share is mounted as a network drive in WinPE and installation is performed over the network. Otherwise, the required Windows installation files are copied to the local hard disk in the opsi-linux-bootimage and installation is performed from the local files. - winpe_uilanguage
-
Display language used under Windows PE.
- winpe_uilanguage_fallback
-
Fallback display language under Windows PE if the primary language is not available.